Part II: Mastering Prompt Engineering for Faculty
This post introduces strategies for creating powerful prompts, focusing on an iterative, faculty-friendly process.
Overwhelmed by Generative AI? You're Not Alone
As a university faculty member, you already juggle teaching, research, and service commitments. Now, generative AI and prompt engineering are making waves. Another thing to learn? Is it any wonder that we feel overwhelmed and would rather just not try it?
But what if this new skill could simplify your work rather than add to it? In this post, I’ll break down prompt writing into manageable strategies, cutting through jargon to help you leverage AI effectively.
In this post, I’ll introduce my strategies for creating powerful prompts, focusing on an iterative, faculty-friendly process.
The strength of generative AI is in the connections it can make between vastly different concepts and domains. It is a great tool for enhancing divergent thinking.1 As Klebahn of Stanford University suggests, “Think about it as an option engine, not an answer engine.”2.
The ability to make unique connections can only happen when the AI tool is given the scope to do so. Wide prompting allows you to do this. With wide prompting, we give a broad, open-ended prompt, which allows the tool to draw from various domains and generate a wide range of responses. Narrow prompting, on the other hand, gives focused and detailed prompts that provide a more precise response. However, the creative element can be lost here.
For example, when I prompted ChatGPT to “Give me some educational activities,” I got activity suggestions for younger children, older children, teens, and adults. One suggestion for younger children was an Alphabet Scavenger Hunt. While this might not seem relevant to college students, it opens possibilities. Maybe I could create a scavenger hunt for my learners. This then leads me to ask ChatGPT to design a scavenger hunt for my learners on a particular topic. I then iteratively focus on specific details to get a precise response for my students.
This process has derogatively been called “blind prompting”3. But this opens up possibilities. That said, this process takes time and might not be suitable for all situations. For example, if you want to generate medical exam questions, you want to narrow down to the subject area and the type of questions you want.
Pro Tip: Start wide to generate ideas, then narrow down for targeted results.
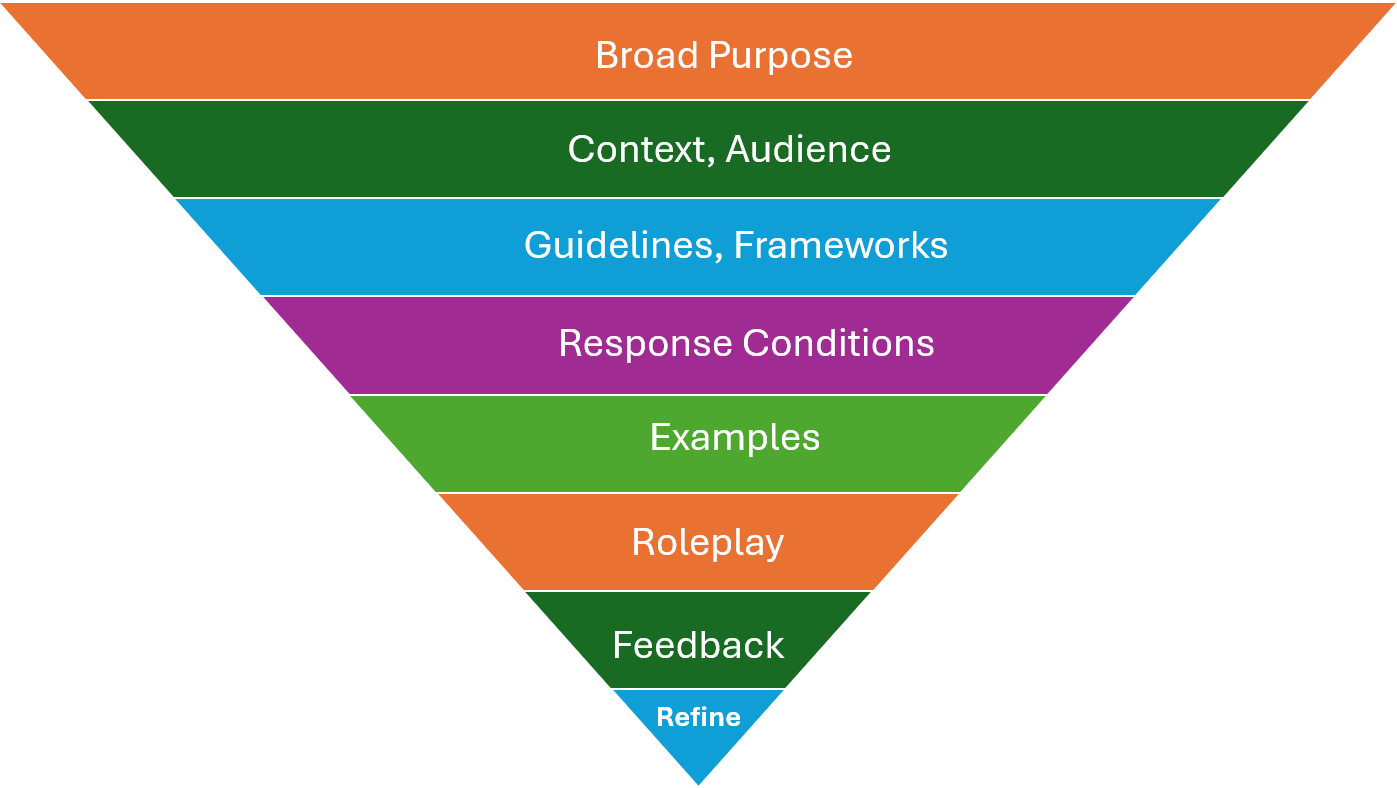
The 7 Elements of Effective Prompting
From my experience with prompting, I’ve identified seven pieces of prompting that are helpful for faculty. These elements are flexible and can be combined based on your needs:
Broad Purpose
Define your goal upfront.
Example: “I want to create a reflective assignment.”
Context and Audience
Describe the situation or background that informs the prompt, and specify who the audience or participants are.
Example: “This is for a 6-week graduate-level course in educational policy.”
Guidelines and Frameworks
Outline any rules, limitations, or structures that the response should adhere to. Example: “Use Gibbs’ reflective cycle framework.”
Response Conditions
Define the tone, format, and expectations.
Example: “Use an empathetic and motivational tone. The assignment is worth 20% of the final grade. The reflection should be about 2-3 pages. Include assignment rubrics in a table format.”
Examples
Provide a sample to clarify expectations (optional). This can be limiting and narrow the focus of the assignment. Therefore, it’s optional and recommended for specific situations where you want the response to be in a certain linguistic style or format.
Example: “Refer to the attached assignment for format guidance.”
Roleplay
Ask the AI to adopt a persona or role.
Example: “You are an experienced lecturer designing assignments.”
Elicit feedback & Refine
Iteratively improve responses by eliciting feedback from the AI tool. Ask ChatGPT to critique the response generated and ask for suggestions for improvement.
Example: “What weaknesses do you see in this assignment? How can I improve it?”
With an iterative approach, where I put in these prompts individually, I get multiple versions of the assignment that I can draw from.
Narrow Prompting
All these prompts can, of course, be combined into one narrow prompt.
I want to create a reflective assignment. This is for a 6-week graduate level course in the educational policy program. Use Gibbs’ reflective cycle framework. Use an empathetic and motivational tone. The assignment is worth 20% of the final grade. The reflection should be about 2-3 pages. Include assignment rubrics in a table format. Use the assignment I am uploading as an example. You are an expert lecturer with many years of experience. What are the weaknesses of this assignment? What challenges might students face? How can I address them?
My favorite prompting elements are:
Starting broad and asking ChatGPT to critique its response from the perspective of an expert.
Try this approach and see how it works for you. Post a comment on how well it worked or didn’t work!!!
Insider Tip:
In Part I, I noted that LLMs are better at crafting prompts than we are. Therefore, I have customized my ChatGPT to begin all conversations by refining my prompt and asking me to choose the prompt I want to use. My simple instruction is:
I want you to begin all conversations by suggesting better versions of my prompt.
Then let me decide which prompt to use.
ChatGPT also offers the option for custom instructions. I do not use this as I find it limits the scope of responses I get.
The Big Picture
Prompt engineering isn’t just another skill to master—it’s a tool to save time and unleash creativity. By starting broad and iterating, you can turn generative AI into a trusted collaborator.
Generative AI isn’t here to replace educators; it’s here to empower us. With thoughtful prompting, you can tackle tasks more effectively and free up time for what matters most—teaching and mentoring.
Call to Action
How will you incorporate these strategies into your workflow? Try them and share your experience in the comments! If you found this helpful, subscribe for more insights on using AI in education.